41 dosage calculations from medication labels
Nursing Pharmacology: Dosage and Calculations Practice Test The medication label reads "1,200,000 units per 2 mL." The nurse has determined that the dose prescribed is safe. The nurse administers how many milliliters per dose to the child? a. 0.8 mL b. 1.2 mL c. 1.4 mL d. 1.7 mL 19. Atropine sulfate, 0.6 mg intramuscularly, is prescribed for a child preoperatively. Nursing Math - Parenteral Injectable Drug Dosage Calculator Parenteral Drug Dosage Calculator For Syringe Liquid Solutions Medicine Injectable Dosage Equations Formulas. Description: This calculator determines the liquid or solution volume to be injected by syringe into the patient. The label on the medicine bottle states the concentration of the medicine. The concentration is the mass of medicine ...
How to Read a Medication Label Nursing Quiz - Registered Nurse RN According to the medication label, what is the dosage strength of this medication? A. 7 g B. 100 mL C. 80 mL D. 350 mg/5 mL The answer is D. Dosage strength is the amount of drug that is in the specific dosage form supplied. 5. How is this medication supplied according to the medication label? A. Capsule B. Injection Solution C. Oral Solution

Dosage calculations from medication labels
Lecture 3: Reading Medication Labels and Basic Dosage Calculations Every tenth of a mLis marked on the syringe, and every half mL is labeled; this means that any dosage we plan to measure using a 3 mL syringe should be rounded to the nearest tenth. Dosages between 1-3 mLshould always be measured in a 3 mL syringe. Drug Dosage Calculations | How-to-guide + Quiz | KnowledgeDose What is the correct dosage on the label? Take 800 units (0.4ml) once daily Take 800 units (0.8ml) once daily Take 800 units (0.6ml) once daily Take 800 units (1ml) once daily About KnowledgeDose Medical Dosage Calculations For Dummies Cheat Sheet flow rate (mL/hr) = total volume (mL) ÷ infusion time (hr) flow rate (mL/hr) = 1,000 ÷ 4 flow rate (mL/hr) = 250 The flow rate is 250 mL/hr. Common conversion factors in medical dosage calculations As a healthcare professional, you have to convert patient weights, fluid volumes, medication weights, and more.
Dosage calculations from medication labels. Dosage Calculations: NCLEX-RN || RegisteredNursing.org Medication label: 1 tablet = 250 mg How many tablets should be administered daily? In this problem you have to determine how many tablets the patient will take if the doctor order is 125 mg a day and the tablets are manufactured in tablets and each tablet has 250 mg. This problem can be set up and calculated as shown below. Solve Alligation Calculations - Pharmacy Tech Review Solve Alligation Calculations. Alligation is solving calculations involving mixtures of the same product with different strengths. Alligation works for liquids, creams, gels, solutions, etc. This is useful for a compounding recipe that calls for an ingredient with a certain strength, but you have other strengths in stock, one of which is less ... Drug Calculations: How To Use Dimensional Analysis Step 3: The desired dose is 0.5 mg. Place information with the same label as the preceding denominator into the equation in the numerator to cancel out the unwanted labels. Repeat this step sequentially until all unwanted labels are canceled out. Step 4. Multiply numbers across the numerator, then multiply all the numbers across the denominator. Chapter 6 Oral Medication Labels and Dosage Calculation Chapter 9 Parenteral Medication Labels and Dosage Calculation; Chapter 36 Calculation of Medication Dosage and Medication; Pharmaceutical Dosage forms Pharmaceutical Dosage forms Definition Dosage; FOOD LABELS Food Labels Food labels help us; Dosage Calculation Pro Calc Nursing 131 Calculating dosage;
PDF Formulas for Calculating Medication Dosage the medication label, and Q (quantity) is the volume in which the dosage strength is available (e.g. tablets, capsules, milliliters). For example: we have an order for Ceclor 0.5 g PO b.i.d. We have available 250 mg capsules. The first thing to do is get like units of measurement. Since we have 250 mg capsules, let's change our ordered dose ... Delmar Cengage Learning Companions - Math for Meds, Dosages and Solutions Chapter 9: Parenteral Medication Labels and Dosage Calculation / 104; Chapter 10: Reconstitution of Powdered Drugs / 126; Chapter 11: Measuring Insulin Dosages / 142; SECTION 4: DOSAGE CALCULATIONS; Chapter 12: Ratio and Proportion / 164; Chapter 13: Dimensional Analysis / Units Conversion / 196; Dosage Calculation Resources - Calhoun Community College Calculation problems will be fill-in-the-blank, NOT multiple choice. If you need testing accommodations contact Student Disability Services at 256-306-2630; Study Guides. Session 1 Basic Review; Session 2 Systems of Measurement.pptx; Session 3 Methods of Administration 2; Session 4 Medication Labels; Session 5 Formula Method and Ratio to ... Nurse's Role and Responsibilities in Administration of Medication Medication may be defined as a substance used to promote health, to prevent disease to diagnose a disease to alleviate or cure diseases. Objectives Nature of the drug i.e. the name, classification, types of preparations, effects, dosage, absorption and excretion, routes of administration, time of administration and indications. Essential parts ...
Dosage Calculator - How to Calculate Dosage? Determine the dosage of the medication. Let's say the appropriate dosage of the active substance is 2 mg/kg of body weight. Weigh yourself. Let's assume you weigh 80 kg. Multiply these two values to get the dose of medication in mg: 2 * 80 = 160 mg. You need to take 160 mg of active substance. What if your medication is liquid? Drug Calculations Involving Reading Drug Labels, Part 1 - YouTube Practice performing drug dosage problems that require the use and understanding of drug labels to solve. Problem 1.) Determine the milliliters of Augmentin required. Problem 2.) Determine the... Dosage Calculation Reading Drug Labels - StuDocu Calculation: Reading Drug Labels Chapter 11 Tarleton State University NURS 3310 Dr. Mary B. Winton Reading Drug Labels a. Brand/trade name b. Generic name c. Formulation d. Dosage strength e. Route f. Need prescription or Over -the-counter Pre-Reg Pharmacy Exam Calculations | ResourcePharm 22.09.2021 · Drug Dosage Calculations. This handout covers a variety of numeracy based tasks which nurses and midwives may be required to perform in practice. These include drug calculations and setting drip rates on the controls of intravenous infusion controllers. The handout covers the following: SI units and conversions, calculating drug quantities in both …
Pharmacy Dosage Calculations - Pharmacy Tech Review Parenteral means medication is delivered by other routes other than orally/gastrointestinal tract. In many cases, this means an injection (remember there are several types of injections!) Commonly, injectable medication strengths are in terms of milligrams per milliliter e.g. clindamycin 300mg/2mL. Understandably, these math problems can be a ...
Clinical Calculations: Module 6: Divided Doses and Reconstituted ... Your charge nurse recommends that you use 1.8 ml of sterile water to reconstitute the medication to reduce the volume to be injected. How many ml will you give per dose? SF = 2 g AU = ml per dose Equivalents: 1 g = 1000 mg 400 mg = 1 ml (from the reconstitution directions on the label)
Drug Calculations: How to Calculate Drops Per Minute 06.12.2021 · 2. Next we add the drip factor for the tubing set we are using. Then alternate the labels until they cancel out. Add the infusion rate (mL/hour), followed by the time (1 hour over 60 minutes). Cancel the labels. What you are left with are …
Reading Medication Labels | Basicmedical Key CHAPTER 13 Reading Medication Labels Objectives After reviewing this chapter, you should be able to identify: 1. The trade and generic names of medications 2. The dosage strength of medications 3. The form in which a medication is supplied 4. The total volume of a medication container where indicated 5. Directions for mixing or preparing a drug where necessary 6.
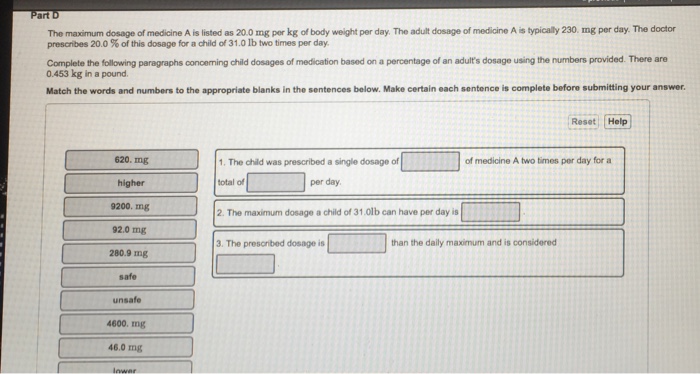
Introductory Level Drug Dosage Practice Problems 27. The doctor prescribes a daily dosage of 500 mg for a patient to be divided into two doses. Find the amount of medication in mL required for an individual dose for this patient by using the label below. Give: _____ mL Figure 2: Mycobutin (rifabutin capsules, USP) [Jpeg]. (2013). Dosage Calculations for Nurses: Know Your Labels.
Drug Calculations Practice NCLEX Questions (100+ Items) - Nurseslabs Methods for Drug Dosage Calculations Standard Method The commonly used formula for calculating drug dosages. Where in: D = Desired dose or dose ordered by the primary care provider. H = dose on hand or dose on the label of bottle, vial, ampule. V = vehicle or the form in which the drug comes (i.e., tablet or liquid). STANDARD FORMULA
Dosage Calculation Using the Ratio and Proportion Method When setting up the ratio and proportion using the fraction format to calculate dosages, the known ratio is what you have available, or the information on the medication label, and is stated first (placed on the left side of the proportion). The desired, or what is ordered to be administered, is the unknown (placed on the right side).
Dose Calculation Dimensional Analysis Factor-Label Method Three primary methods for calculation of medication dosages exist, and these include dimensional analysis, ratio proportion, and formula or desired-over-have method. This article explores dimensional analysis in more detail. Dimensional analysis, as the name represents, explores dimensions or units of measurements called factors.
Dose Calculation Desired Over Have Formula Method - StatPearls - NCBI ... A basic formula, solving for x, guides us in the setting up of an equation: D/H x Q = x, or Desired dose (amount) = ordered Dose amount/amount on Hand x Quantity. For example, a provider requests lorazepam 4 Mg IV Push for a patient in severe alcohol withdrawal. The clinician has 2 mg/mL vials on hand.
6.2 Safe Medication Administration – Clinical Procedures for … Be diligent in all medication calculations. Errors in medication calculations have contributed to dosage errors, especially when adjusting or titrating dosages. Avoid reliance on memory; use checklists and memory aids. Slips in memory are caused by lack of attention, fatigue, distractions. Mistakes are often referred to as attentional ...
(PDF) Pharmaceutical Calculations 13th - Ansel - Academia.edu Pharmaceutical Calculations 13th - Ansel. × Close Log In. Log in with Facebook Log in with Google. or. Email. Password. Remember me on this computer. or reset password. Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link. Need an account? Click here to sign up. Log In Sign Up. Log In; Sign Up; more ...
Calculating from the labels | Learning Lab Calculating from the labels. This short video is the second of three videos in the Nursing calculations - Finding the volume required section. It explains how to calculate medication dosage from labels using the method of mental calculation and proportinality to get the right dosage for drugs in solution. YouTube. RMIT University Library Videos.

Dosage Calculation Help & Review. | Be A Nurse | Pinterest | Dosage calculations, Pharmacology ...
Dosage Calculations Made Easy | Reconstitution Calculation Medication ... Dosage Calculations Nursing Students: This video demonstrates how to solve dosage and calculation problems for reconstitution of medications. I use dimension...
PDF Basic Medication Calculations 10. Medication: 400mg of Dopamine Volume of Fluid: 250 ml Order is in: mcg 11. Medication: 2g of Lidocaine Volume of Fluid: 1000ml Order is in: mg 12. Medication: 5g of Bretylium Volume of Fluid: 500ml Order is in: mg 13. Medication: 1600mcg Dopamine Volume of Fluid: 1000ml Order is in: mcg 14. Medication: 2mg of Lidocaine Volume of Fluid: 250ml
Ansel's Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms and Drug Delivery … Ansel's Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms & Drug Delivery System, 9th Edition , 2011. Eman Hamdy. Download Download PDF. Full PDF Package Download Full PDF Package. This Paper. A short summary of this paper. 37 Full PDFs related to this paper. Read Paper. Download Download PDF. Download Full PDF Package ...
Chapter 53. Medication Administration Flashcards | Quizlet To administer drugs safely and effectively to all patient groups, including pediatric, pregnant, and elderly patients, you must know and understand the principles of pharmacology (see the Principles of Pharmacology chapter) and how to perform dosage calculations (see the Dosage Calculation chapter). This chapter prepares you to understand the fundamentals of drug …
PDF Medication Calculation Examination Study Guide Label shows 75 - 150 mg/kg per day. Is the physician's order within normal range? Solution: 6 x 75 = 450 mg (minimum dosage per day); 150 X6 = 900 (maximum dosage per day) 24 ÷ 4 = 6 dosages : 300 x 6 = 1800. Answer: Dosage is not within range. IV Calculations • [amount of fluid to be infused] x [drop factor] ÷ minutes to infuse = gtts/min










Post a Comment for "41 dosage calculations from medication labels"